- Published on
DeepAgents 深度解析:从概念到代码验证的完整指南
- Authors

- Name
- Shoukai Huang

DeepAgents(Photo by Micah & Sammie Chaffin on Unsplash)
快速导航本篇内容:
概述
在人工智能快速发展的今天,构建智能代理系统已成为开发者关注的焦点。DeepAgents 作为 LangChain 生态系统中的重要组成部分,为开发者提供了一个强大而易用的代理工具包。本文将从概念理解到代码实践,全面解析 DeepAgents 的技术特性与应用场景。
1. DeepAgents 核心概念
DeepAgents 是由 LangChain 团队开发的开源 Python 工具包,专门用于构建能够处理复杂任务的智能 AI 代理。它基于 LangGraph 构建,并受到 Claude Code、Deep Research 和 Manus 等先进应用程序的启发,为开发者提供了一套完整的代理构建解决方案。
四大核心能力
1. 智能规划与任务分解 DeepAgents 内置 write_todos 工具,使代理能够:
- 将复杂任务分解为离散的执行步骤
- 实时跟踪任务执行进度
- 根据新信息动态调整执行计划
2. 高效上下文管理 通过文件系统工具集(ls、read_file、write_file、edit_file),代理可以:
- 将大型上下文信息卸载到外部存储
- 有效防止上下文窗口溢出问题
- 处理可变长度的工具执行结果
3. 子代理生成机制 内置的 task 工具支持:
- 生成专门化的子代理处理特定任务
- 实现上下文隔离,保持主代理环境整洁
- 深入执行复杂的子任务流程
4. 长期记忆能力 利用 LangGraph 的 Store 功能:
- 为代理扩展跨线程持久内存
- 保存和检索历史对话信息
- 支持多会话间的知识共享
与 LangChain 生态系统的关系
DeepAgents 在 LangChain 生态系统中扮演着重要角色,它与其他组件形成了完整的技术栈:
核心依赖关系:
- LangGraph:提供底层图形执行引擎和状态管理机制
- LangChain:提供工具集成和模型抽象,与 DeepAgents 无缝协作
- LangSmith:通过 LangGraph 平台实现系统可观察性和生产部署
2. 技术架构定位:DeepAgents、LangChain 和 LangGraph
为了更好地理解这三个组件的关系,我们可以将它们类比为不同层次的技术解决方案:
- LangChain:代理框架层 - 提供标准化的开发抽象
- LangGraph:代理运行时层 - 负责底层执行和状态管理
- DeepAgents:代理工具包层 - 提供开箱即用的完整解决方案
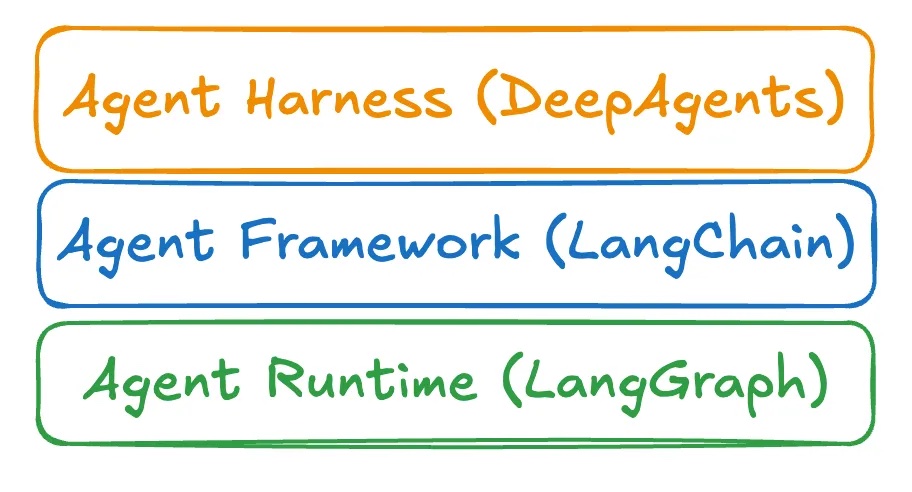
DeepAgents 在技术架构中的定位关系
LangGraph:代理运行时层
LangGraph 作为代理运行时,专注于提供底层的图形执行引擎和状态管理能力。
核心职责: 当您需要在生产环境中运行代理时,需要可靠的代理运行时支持。LangGraph 提供了完整的基础设施层面考虑:
- 持久化执行:支持长时间运行的代理任务
- 流式传输支持:实时数据流处理能力
- 人机交互支持:支持人工干预和监督
- 线程级持久化:单个会话内的状态保持
- 跨线程持久化:多会话间的数据共享
技术定位: LangGraph 的设计理念借鉴了 Temporal、Inngest 等持久执行引擎,专注于为代理框架提供可靠的底层运行时支持。
LangChain:代理框架层
LangChain 作为代理框架,主要价值在于提供标准化的开发抽象。
核心价值:
- 抽象化设计:将复杂的 LLM 交互抽象为易用的接口
- 标准化开发:提供统一的应用构建方法
- 简化入门:降低开发者的学习和使用门槛
- 项目迁移:支持开发人员在不同项目间轻松迁移
设计理念: 优秀的抽象应该简化复杂性而不是增加复杂性。LangChain 1.0 构建于 LangGraph 之上,充分利用其代理运行时能力,为开发者提供更高层次的开发体验。
DeepAgents:代理工具包层
DeepAgents 是 LangChain 团队的最新项目,它比代理框架更高层次——直接构建于 LangChain 之上。
独特优势:
- 预设提示词:内置优化的提示词模板
- 工具调用处理:自定义的工具调用逻辑
- 规划工具集:内置任务规划和分解能力
- 文件系统访问:完整的文件操作支持
- 开箱即用:自带"电池"的完整解决方案
产品定位: DeepAgents 可以理解为"通用版的 Claude Code"。它不仅仅是一个框架,而是一个完整的代理工具包,为开发者提供了构建复杂代理系统的所有必要组件。
三者详细对比
Agent Frameworks(代理框架)、Agent Runtimes(代理运行时) 和 Agent Harnesses(代理工具包) 的详细对比
| 层级 | 代表工具/框架 | 中文解释与价值点 | 典型使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工具包层 (Harness) | DeepAgents Claude Agent SDK | 开箱即用的完整解决方案 • 预设提示词和工具 • 内置子代理生成 • 完整的文件系统支持 • 高度封装,开发效率最高 | 快速原型开发 • 构建自主研究代理 • 自动化报告生成 • 复杂任务自动化 • 需要快速上线的项目 |
| 框架层 (Framework) | LangChain CrewAI Google ADK OpenAI Agents SDK LlamaIndex Vercel AI SDK | 标准化开发抽象 • 统一的工具调用接口 • 标准化的链式操作 • 模块化的组件设计 • 便于团队协作和维护 | 企业级应用开发 • 需要灵活组合的项目 • 团队协作开发 • 自定义业务逻辑 • 多模型集成场景 |
| 运行时层 (Runtime) | LangGraph Temporal Inngest | 生产级执行保障 • 持久化状态管理 • 断点续跑机制 • 流式输出支持 • 人机交互回路(HITL) • 适合长时间、有状态任务 | 生产环境部署 • 长时间运行的代理 • 高可靠性要求 • 复杂工作流编排 • 需要监控和调试的系统 |
一句话总结:
- Harness 像“整机”,拿来就用;
- Framework 像“主板”,按需插拔;
- Runtime 像“电源+冷却”,保证任务不熄火。
3. 快速入门
首先安装必要的依赖包:
uv add deepagents tavily-python python-dotenv langchain-deepseek
在工程根目录下创建 .env 文件,配置 API 密钥:
DEEPSEEK_API_KEY=sk-xxx
TAVILY_API_KEY=tvly-dev-xxx
基础示例:构建研究代理
以下代码展示了如何使用 DeepAgents 结合 DeepSeek 和 Tavily 构建一个具备网络搜索能力的研究代理:
import os
from typing import Literal
from tavily import TavilyClient
from deepagents import create_deep_agent
from langchain_deepseek import ChatDeepSeek
# 加载环境变量
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
tavily_client = TavilyClient(api_key=os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"])
# 初始化 DeepSeek 模型
deepseek_model = ChatDeepSeek(
model="deepseek-chat", # 使用 DeepSeek-V3,支持工具调用和结构化输出
api_key=os.environ["DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"],
temperature=0.1,
)
def internet_search(
query: str,
max_results: int = 5,
topic: Literal["general", "news", "finance"] = "general",
include_raw_content: bool = False,
):
"""Run a web search"""
return tavily_client.search(
query,
max_results=max_results,
include_raw_content=include_raw_content,
topic=topic,
)
# System prompt to steer the agent to be an expert researcher
research_instructions = """You are an expert researcher. Your job is to conduct thorough research and then write a polished report.
You have access to an internet search tool as your primary means of gathering information.
## `internet_search`
Use this to run an internet search for a given query. You can specify the max number of results to return, the topic, and whether raw content should be included.
"""
agent = create_deep_agent(
tools=[internet_search],
system_prompt=research_instructions,
model=deepseek_model # 使用 DeepSeek 模型
)
result = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is langgraph?"}]})
# Print the agent's response
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
运行结果
执行命令 uv run deepagents_samples.py,可以看到代理成功调用了网络搜索工具,并生成了关于 LangGraph 的详细报告:
Based on my research, here's a comprehensive overview of what LangGraph is:
## What is LangGraph?
**LangGraph** is an open-source framework within the LangChain ecosystem designed for building **stateful, multi-actor applications** using Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a structured approach to creating complex agent and multi-agent workflows with fine-grained control over both the flow and state of applications.
## Key Features and Capabilities
### 1. **State Management**
- Maintains persistent state across multiple agent interactions
- Enables agents to remember context and build upon previous interactions
- Supports complex, long-running workflows that require memory
### 2. **Multi-Agent Coordination**
- Orchestrates multiple AI agents working together
- Manages parallel execution of agents
- Coordinates information sharing between agents through centralized state
### 3. **Graph-Based Architecture**
- Models workflows as directed graphs where nodes represent agents or operations
- Supports conditional workflows that alter execution paths based on agent outputs
- Provides fine-grained control over workflow logic
### 4. **Human-in-the-Loop Integration**
- Allows human intervention and oversight in agent workflows
- Supports real-time monitoring and debugging
- Enables manual approval or modification of agent decisions
## Primary Use Cases
LangGraph is particularly well-suited for:
- **Complex multi-agent systems** where multiple specialized agents need to collaborate
- **Stateful applications** that require memory and context across interactions
- **Custom agent architectures** with unique logic and workflow requirements
- **Production-ready agent systems** that need reliability and monitoring
- **Task automation tools** with complex, conditional workflows
## Technical Foundation
- Built on top of LangChain's ecosystem
- Available in both Python and JavaScript
- Supports integration with various LLM providers
- Provides APIs and tools for deployment and monitoring
- Used by companies like GitLab, Elastic, Cisco, and Vodafone in production
## Why Use LangGraph?
LangGraph addresses the challenges of building sophisticated LLM applications by providing:
- **Structured coordination** of multiple agents
- **State persistence** across complex workflows
- **Fine-grained control** over agent behavior
- **Production-ready** deployment capabilities
- **Flexible architecture** for custom requirements
In essence, LangGraph moves beyond simple LLM integrations to enable the creation of truly sophisticated, stateful agent systems capable of handling complex, real-world tasks that require coordination, memory, and conditional logic
深入理解:添加日志追踪
由于 DeepAgents 进行了高度封装,为了更好地理解其内部工作机制,我们可以添加日志记录来观察模型的调用和执行过程:
import os
import logging
import json
from typing import Literal
from tavily import TavilyClient
from deepagents import create_deep_agent
from langchain_deepseek import ChatDeepSeek
from langchain_core.callbacks import BaseCallbackHandler
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from langchain_core.outputs import LLMResult
# 加载环境变量
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler('deepagents.log'),
logging.StreamHandler()
]
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# 自定义回调处理器来记录模型交互
class DeepSeekLoggingCallback(BaseCallbackHandler):
"""自定义回调处理器,用于记录 DeepSeek 模型的完整交互过程"""
def on_llm_start(self, serialized, prompts, **kwargs):
"""记录模型调用开始"""
logger.info("=== DeepSeek 模型调用开始 ===")
try:
logger.info(f"序列化信息: {json.dumps(serialized, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)}")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"序列化信息: {str(serialized)} (序列化失败: {e})")
for i, prompt in enumerate(prompts):
logger.info(f"输入提示 {i+1}: {prompt}")
if kwargs:
try:
logger.info(f"额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)}")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"额外参数: {str(kwargs)} (序列化失败: {e})")
def on_llm_end(self, response: LLMResult, **kwargs):
"""记录模型调用结束"""
logger.info("=== DeepSeek 模型调用结束 ===")
for i, generation in enumerate(response.generations):
for j, gen in enumerate(generation):
output_text = gen.text
logger.info(f"输出结果 {i+1}-{j+1}: {output_text}")
# 记录生成信息(如果可用)
if hasattr(gen, 'generation_info') and gen.generation_info:
try:
logger.info(f"生成信息 {i+1}-{j+1}: {json.dumps(gen.generation_info, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)}")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"生成信息 {i+1}-{j+1}: {str(gen.generation_info)}")
# 记录使用的 token 数量(如果可用)
if hasattr(response, 'llm_output') and response.llm_output:
try:
logger.info(f"LLM 输出信息: {json.dumps(response.llm_output, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)}")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"LLM 输出信息: {str(response.llm_output)}")
if kwargs:
try:
logger.info(f"额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2, default=str)}")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"额外参数: {str(kwargs)}")
def on_llm_error(self, error, **kwargs):
"""LLM 出错时调用"""
logger.error(f"=== DeepSeek 模型调用出错 ===")
logger.error(f"错误信息: {str(error)}")
logger.error(f"错误类型: {type(error).__name__}")
if kwargs:
logger.error(f"额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_llm_new_token(self, token: str, **kwargs):
"""记录新生成的 token"""
logger.info(f"新生成 token: '{token}'")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"Token 额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_chain_start(self, serialized, inputs, **kwargs):
"""记录链调用开始"""
logger.info("=== 链调用开始 ===")
logger.info(f"链序列化信息: {json.dumps(serialized, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
logger.info(f"链输入: {json.dumps(inputs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"链额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_chain_end(self, outputs, **kwargs):
"""记录链调用结束"""
logger.info("=== 链调用结束 ===")
logger.info(f"链输出: {json.dumps(outputs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"链额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_chain_error(self, error, **kwargs):
"""记录链调用出错"""
logger.error(f"=== 链调用出错 ===")
logger.error(f"错误信息: {str(error)}")
logger.error(f"错误类型: {type(error).__name__}")
if kwargs:
logger.error(f"链额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_tool_start(self, serialized, input_str, **kwargs):
"""记录工具调用开始"""
logger.info("=== 工具调用开始 ===")
logger.info(f"工具序列化信息: {json.dumps(serialized, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
logger.info(f"工具输入: {input_str}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"工具额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_tool_end(self, output, **kwargs):
"""记录工具调用结束"""
logger.info("=== 工具调用结束 ===")
logger.info(f"工具输出: {output}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"工具额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_tool_error(self, error, **kwargs):
"""记录工具调用出错"""
logger.error(f"=== 工具调用出错 ===")
logger.error(f"错误信息: {str(error)}")
logger.error(f"错误类型: {type(error).__name__}")
if kwargs:
logger.error(f"工具额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_text(self, text, **kwargs):
"""记录文本输出"""
logger.info(f"=== 文本输出 ===")
logger.info(f"文本内容: {text}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"文本额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_retry(self, retry_state, **kwargs):
"""记录重试"""
logger.info(f"=== 重试操作 ===")
logger.info(f"重试状态: {retry_state}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"重试额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
def on_custom_event(self, name, data, **kwargs):
"""记录自定义事件"""
logger.info(f"=== 自定义事件: {name} ===")
logger.info(f"事件数据: {json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
if kwargs:
logger.info(f"事件额外参数: {json.dumps(kwargs, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)}")
# 创建回调处理器实例
deepseek_callback = DeepSeekLoggingCallback()
tavily_client = TavilyClient(api_key=os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"])
# 初始化 DeepSeek 模型
logger.info("初始化 DeepSeek 模型...")
deepseek_model = ChatDeepSeek(
model="deepseek-chat", # 使用 DeepSeek-V3,支持工具调用和结构化输出
api_key=os.environ["DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"],
temperature=0.1,
callbacks=[deepseek_callback] # 添加回调处理器
)
logger.info(f"DeepSeek 模型初始化完成: model=deepseek-chat, temperature=0.1")
def internet_search(
query: str,
max_results: int = 5,
topic: Literal["general", "news", "finance"] = "general",
include_raw_content: bool = False,
):
"""Run a web search"""
logger.info("=== Tavily 网络搜索开始 ===")
logger.info(f"搜索参数:")
logger.info(f" - 查询内容: '{query}'")
logger.info(f" - 最大结果数: {max_results}")
logger.info(f" - 搜索主题: '{topic}'")
logger.info(f" - 包含原始内容: {include_raw_content}")
try:
result = tavily_client.search(
query,
max_results=max_results,
include_raw_content=include_raw_content,
topic=topic,
)
logger.info("=== Tavily 网络搜索结果 ===")
results_count = len(result.get('results', []))
logger.info(f"搜索完成,返回 {results_count} 个结果")
# 记录每个搜索结果的详细信息
for i, search_result in enumerate(result.get('results', []), 1):
logger.info(f"结果 {i}:")
logger.info(f" - 标题: {search_result.get('title', 'N/A')}")
logger.info(f" - URL: {search_result.get('url', 'N/A')}")
logger.info(f" - 评分: {search_result.get('score', 'N/A')}")
# 记录内容摘要
content = search_result.get('content', '')
if content:
logger.info(f" - 内容摘要: {content}")
else:
logger.info(f" - 内容摘要: 无内容")
# 如果包含原始内容,也记录完整内容
if include_raw_content and 'raw_content' in search_result:
raw_content = search_result.get('raw_content', '')
if raw_content:
logger.info(f" - 原始内容: {raw_content}")
else:
logger.info(f" - 原始内容: 无原始内容")
# 记录搜索查询信息(如果可用)
if 'query' in result:
logger.info(f"实际执行的查询: '{result['query']}'")
logger.info("=== Tavily 网络搜索完成 ===")
return result
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"=== Tavily 网络搜索失败 ===")
logger.error(f"错误信息: {str(e)}")
logger.error(f"搜索参数: query='{query}', max_results={max_results}, topic='{topic}'")
raise
# System prompt to steer the agent to be an expert researcher
research_instructions = """You are an expert researcher. Your job is to conduct thorough research and then write a polished report.
You have access to an internet search tool as your primary means of gathering information.
## `internet_search`
Use this to run an internet search for a given query. You can specify the max number of results to return, the topic, and whether raw content should be included.
"""
logger.info("=== 创建 DeepAgent ===")
agent = create_deep_agent(
tools=[internet_search],
system_prompt=research_instructions,
model=deepseek_model # 使用 DeepSeek 模型
)
logger.info("DeepAgent 创建完成")
user_query = "What is langgraph?"
logger.info(f"=== 开始执行用户查询 ===")
logger.info(f"用户问题: '{user_query}'")
result = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_query}]})
logger.info("=== 用户查询执行完成 ===")
logger.info("=== Agent 最终响应 ===")
# 记录完整的对话历史
for i, message in enumerate(result["messages"]):
role = message.role if hasattr(message, 'role') else getattr(message, 'type', 'unknown')
content = message.content if hasattr(message, 'content') else str(message)
logger.info(f"消息 {i+1} ({role}):")
logger.info(f" 内容: {content}")
# Print the agent's response
final_response = result["messages"][-1].content
logger.info("=== 输出最终结果给用户 ===")
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("DeepAgent 响应:")
print("="*50)
print(final_response)
print("="*50)
可以看见完整调用过程,内容过长,不进行展示。其中 DeepAgents 添加的提示词如下。
System: You are an expert researcher. Your job is to conduct thorough research and then write a polished report.
You have access to an internet search tool as your primary means of gathering information.
## `internet_search`
Use this to run an internet search for a given query. You can specify the max number of results to return, the topic, and whether raw content should be included.
In order to complete the objective that the user asks of you, you have access to a number of standard tools.
## `write_todos`
You have access to the `write_todos` tool to help you manage and plan complex objectives.
Use this tool for complex objectives to ensure that you are tracking each necessary step and giving the user visibility into your progress.
This tool is very helpful for planning complex objectives, and for breaking down these larger complex objectives into smaller steps.
It is critical that you mark todos as completed as soon as you are done with a step. Do not batch up multiple steps before marking them as completed.
For simple objectives that only require a few steps, it is better to just complete the objective directly and NOT use this tool.
Writing todos takes time and tokens, use it when it is helpful for managing complex many-step problems! But not for simple few-step requests.
## Important To-Do List Usage Notes to Remember
- The `write_todos` tool should never be called multiple times in parallel.
- Don't be afraid to revise the To-Do list as you go. New information may reveal new tasks that need to be done, or old tasks that are irrelevant.
## Filesystem Tools `ls`, `read_file`, `write_file`, `edit_file`
You have access to a filesystem which you can interact with using these tools.
All file paths must start with a /.
- ls: list all files in the filesystem
- read_file: read a file from the filesystem
- write_file: write to a file in the filesystem
- edit_file: edit a file in the filesystem
## `task` (subagent spawner)
You have access to a `task` tool to launch short-lived subagents that handle isolated tasks. These agents are ephemeral — they live only for the duration of the task and return a single result.
When to use the task tool:
- When a task is complex and multi-step, and can be fully delegated in isolation
- When a task is independent of other tasks and can run in parallel
- When a task requires focused reasoning or heavy token/context usage that would bloat the orchestrator thread
- When sandboxing improves reliability (e.g. code execution, structured searches, data formatting)
- When you only care about the output of the subagent, and not the intermediate steps (ex. performing a lot of research and then returned a synthesized report, performing a series of computations or lookups to achieve a concise, relevant answer.)
Subagent lifecycle:
1. **Spawn** → Provide clear role, instructions, and expected output
2. **Run** → The subagent completes the task autonomously
3. **Return** → The subagent provides a single structured result
4. **Reconcile** → Incorporate or synthesize the result into the main thread
When NOT to use the task tool:
- If you need to see the intermediate reasoning or steps after the subagent has completed (the task tool hides them)
- If the task is trivial (a few tool calls or simple lookup)
- If delegating does not reduce token usage, complexity, or context switching
- If splitting would add latency without benefit
## Important Task Tool Usage Notes to Remember
- Whenever possible, parallelize the work that you do. This is true for both tool_calls, and for tasks. Whenever you have independent steps to complete - make tool_calls, or kick off tasks (subagents) in parallel to accomplish them faster. This saves time for the user, which is incredibly important.
- Remember to use the `task` tool to silo independent tasks within a multi-part objective.
- You should use the `task` tool whenever you have a complex task that will take multiple steps, and is independent from other tasks that the agent needs to complete. These agents are highly competent and efficient.
Human: What is langgraph?
总结
通过本文的深入分析,我们全面了解了 DeepAgents 的核心概念和实际应用:
核心价值:
- 开箱即用:DeepAgents 作为代理工具包,提供了完整的解决方案,大大降低了开发门槛
- 高度集成:基于 LangGraph 运行时和 LangChain 框架,充分利用了成熟的生态系统
- 灵活扩展:支持自定义工具和模型,满足不同场景的需求
技术优势:
- 预设的提示词和工具集合
- 内置的子代理生成能力
- 完整的文件系统操作支持
- 与主流 LLM 提供商的无缝集成
适用场景:
- 快速原型开发和概念验证
- 自动化研究和报告生成
- 复杂任务的智能化处理
- 需要快速上线的 AI 代理项目
DeepAgents 代表了 AI 代理开发的一个重要方向:通过高度封装和标准化,让开发者能够专注于业务逻辑而非底层实现细节。随着 AI 技术的不断发展,这种"工具包"模式将在企业级应用中发挥越来越重要的作用。
参考链接
- Agent Frameworks, Runtimes, and Harnesses- oh my! - LangChain 官方博客关于代理架构的详细解析
- DeepAgents 快速入门 - DeepAgents 官方快速入门指南
- LangGraph 官方文档 - LangGraph 框架完整文档
- DeepSeek API 文档 - DeepSeek 模型 API 使用指南
- Tavily Search API - Tavily 网络搜索服务文档